Data Governance Framework
Establishing strong data governance is critical to improving the state’s overall level of data maturity. By standardizing the approach to managing the way data is collected, accessed, shared, and retained, in alignment with policies and regulations, Maryland will strengthen its position to mitigate security and privacy risks with sustainable, repeatable processes.
The data governance framework establishes the relationship between the various components of data management to create a plan that aligns with, and effectively meets, the business objectives of state agencies. The framework is designed to provide agencies with ownership over their data governance plan, aligning their existing processes with the components of the framework. The framework builds upon state data policies, standards, and procedures with a concentration on people, processes, and technology.
The Data Governance Framework adopted by the State of Maryland includes 6 key elements that are vital to developing effective, sustainable data governance programs. These Elements are:
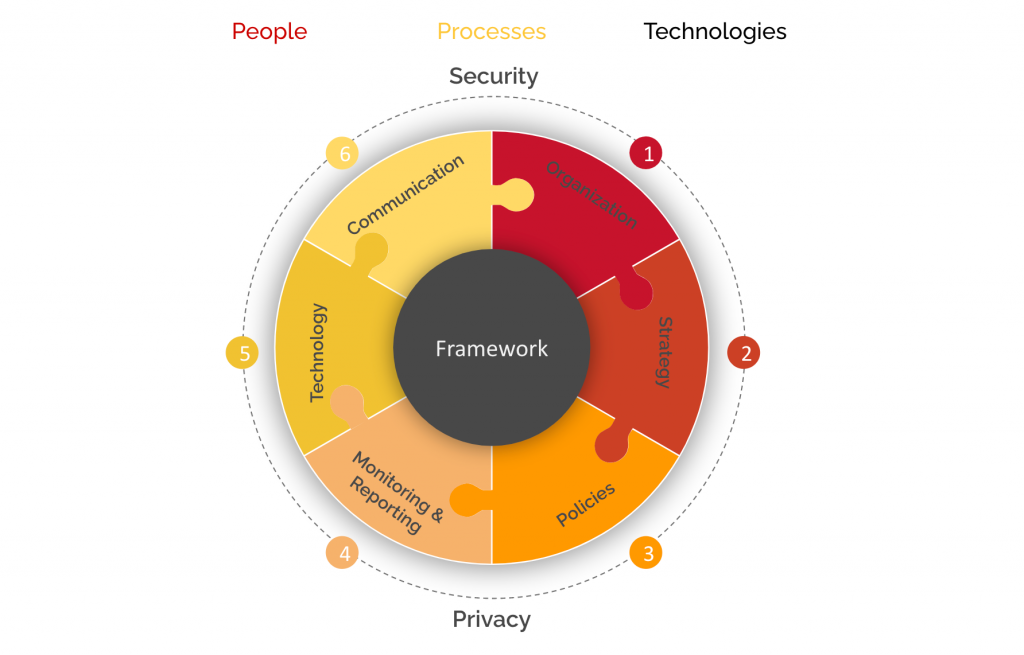
Organization
Data governance requires participation and commitment from all levels of an organization. Active cooperation and partnerships are critical to ensuring that data is available, usable, and secure. The data governance organization is responsible for managing data as an asset to derive value. This consists of individuals and groups that are responsible for specific parts of the data lifecycle. The organization outlines specific data management goals within the organization, such as maintaining data assets, ensuring the privacy of data, understanding the needs of stakeholders, and ensuring the quality of the data. Through explicit assignment of roles and responsibilities, as well as agreed upon rules of engagement, the data governance organization can effectively and confidently manage data assets throughout the varying levels of the organization.
Strategy
The data management strategy consists of understanding what data the organization needs, how it will obtain it, manage it, ensure its reliability, and utilize it with the business objective in order to achieve high-level goals. Specifically, the data management strategy includes parts related to maintaining and improving data quality, data access, data security, and challenges related to data management.
The statewide data strategic plans establish the goals and objectives that collectively the state is looking to achieve. These goals and objectives impact each agency in different ways based on the agency’s data management maturity level, resource availability, and general ability to scale. The agency data governance plan’s strategy should identify the agency’s approach to meeting the statewide goals and objectives.
Policy, Standards, and Procedures Development
Policies, standards, and procedures ensure high-quality data according to governance regulations, standards, and procedures. Data policies are established at a statewide level by the Chief Data Office, Chief Privacy Office, and Office of Security Management. State units may develop additional policies that benefit data management within their organization. As part of the data governance plan development, units will identify the standards and develop procedures to maintain their data assets.
Monitoring and Compliance
Data must be monitored to ensure policies and procedures are followed. Routine checks for items such as metadata can be monitored to ensure naming standards, security, and visibility are consistent with established governance procedures and policies. Agencies will establish monitoring and reporting processes that support continuous improvement of data governance practices. The following areas should be considered, at minimum, when developing data governance plans in alignment with state data policies:
- Quality
- Metadata
- Interoperability and Integration
Technology
Technology relates to the systems that store the data, the data exchange solutions, and the operational and business rule functionality. In addition, technology allows for enhanced data accessibility, sharing, and value. Systems accounting for data storage, operations, analytics, and reporting must be monitored for compliance with policies and procedures. The data governance plan should identify the data management tools and platforms currently being used throughout their organization.
Communication
Establishing a clear communication plan for data governance is a critical component for effectively maintaining broad awareness of data governance initiatives within an organization. The communication plan outlines an engagement model for stakeholders, identifies the type of information shared, and the schedule that information will be released. Proper communication improves the implementation of data strategies and goals, as data governance can be a complex topic. Effectively communicating the data governance plan provides an opportunity to reduce the fear of change, build organizational buy-in and participation, and provide a clear roadmap for implementation.
As part of the data governance plan, Units will develop a plan that will identify the process for effectively communicating the data governance program initiatives to stakeholders across their agency. The plan should include the message; goals/objectives; audience; style; channel, method, medium; timing; frequency; materials; communicators; expected response; metrics; and resource plan.
